Description
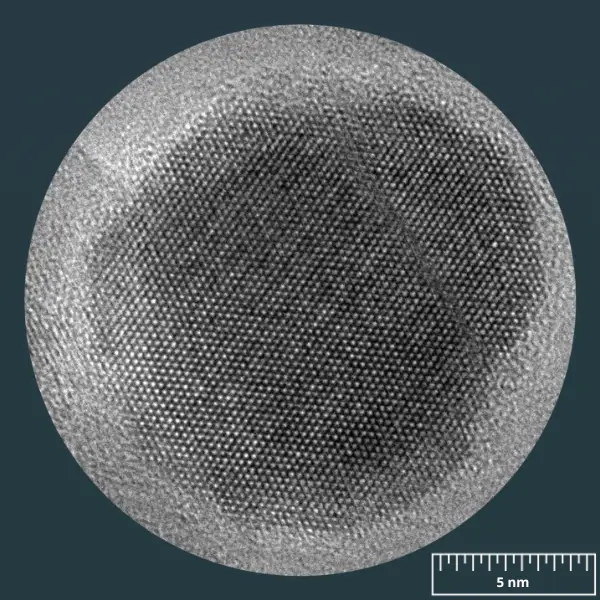
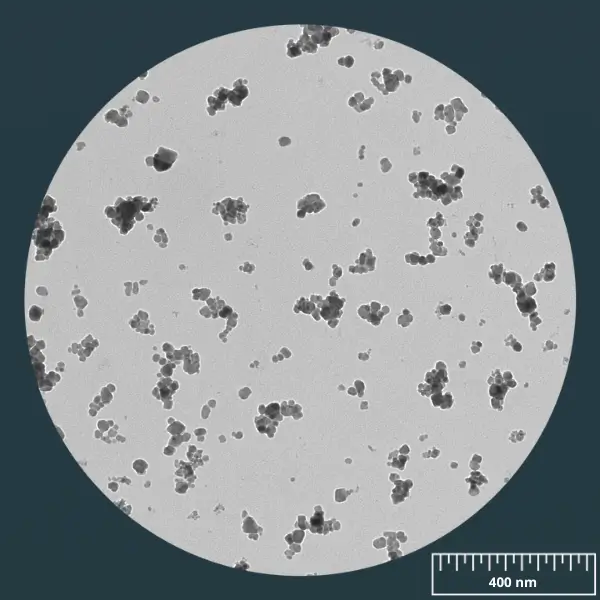
SON’s SPIONs, or iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4), are essential nanomaterials in nanoparticle chemistry.
SPIONs (Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles) truly represent SON’s core skills and feature a range of qualities that are crucial in many fields, from nanomedicine to chemistry.
What is a SPION?
A superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (SPION) is a type of nanoparticle. SPIONs (which are also sometimes called USPIOs or SPIOs — U for Ultra-small) exhibit magnetic properties when exposed to a magnetic field.
What are iron oxide nanomaterials used for?
Their magnetic properties make them particularly useful. They are especially valuable in imaging (notably magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI).
SPIONs are commonly used in medical imaging as contrast agents to improve image resolution and sensitivity. This serves to improve diagnostic accuracy by making results easier to interpret. This means that tumours, inflammatory lesions, and vascular diseases are more clearly visible on the images.
Researchers are also making increasing use of SPIONs to create targeted drugs. Magnetic therapy is also seeing a rapid increase in use.
Iron oxide nanoparticles are used in research to study the biodistribution of drugs, cell-nanoparticle interaction, and various other biological processes.
Why choose SON?
SON is currently proud to offer iron oxide nanoparticles at competitive prices without compromising on quality.